When people refer to ancient empires these days, especially the biggest ones, Rome is invariably brought up. The fall of the Roman Empire is used as an example of greatness toppled by its own avarice, pride, greed, foolishness, or whatever other vice is being explained. The thing is, while the Roman Empire did conquer vast expanses of the world and it did exist for a very long time, in a technical sense it was not actually that big.
Relatively speaking, at under two million square miles, the Roman Empire covered much less space than many other empires. Some of them were so big that they downright dwarfed the Romans.
10. British Empire

No discussion of great empires can start or stop without mention of the British Empire. Hands down, the largest empire in human history. While Rome covered 1.9 million square miles, the British Empire swallowed up 35.5 million square kilometers, or roughly 13.7 million square miles. That’s larger than the entire continent of North America, with Europe tossed in for good measure.
Unlike smaller empires, the British imperial machine was successful because it was willing and able to branch out across the entire globe. Romans could never have claimed Canada as their own, for instance, but the Brits could and did. The empire ruled over about 23% of the entire world’s population and took up 25% of all the land our planet has.
At one time or another the British Empire held sway over India, Australia, Canada, Egypt, Iraq, Jamaica, Botswana, South Africa, Malaysia, Belize, the 13 original US colonies and dozens more. It was represented on every continent on Earth that had people living there.
The Empire began establishing itself back in the 1500s, and it wasn’t until the 1980s that the empire was effectively ended as countries like Canada developed their own constitutions and officially separated from England.
9. Mongol Empire

At 24 million square kilometers, or about 9.3 million square miles, the Mongol Empire was the closest in size to the British Empire that history ever produced. That made it about the size of North America by area. This is made a little more significant by the fact the Empire existed in the 13th and 14th centuries when, unlike the Brits, the Mongols would have had no ability to get to North or South America. The empire was the largest contiguous empire in history.
You could travel from Peking to Moscow to Baghdad and never leave the empire back in the day. Genghis Khan united a number of clans and his forces were nearly unstoppable, sacking cities wherever they traveled and bringing as much of the known world as anyone could imagine under the Empire. They took those who surrendered into the fold and those who didn’t suffered the consequences.
During his lifetime, Genghis Khan oversaw expansion unseen since. It was only after his death that the empire began to crack as internal disputes over who should rule took their toll and the massive size of the Empire proved too hard to manage without everyone working in clear agreement. Battles between his successors saw the empire fall apart, and by the time Kublai Khan died, the whole empire had become four separate ones.
8. Russian Empire

The Russian Empire, at its peak, covered a massive 22.8 million square kilometers, or 8.8 million square miles. Compare that to modern day Russia which, as one of the largest countries on earth, covers 17.1 million square kilometers.
Russian’s empire rose to power in 1721 when Tsar Peter signed the Treaty of Nystad in 1721. Arguably the Empire existed well before that, but it became official at that moment. It lasted until 1917, when the revolution declared the country a republic.
The Russian Empire was obviously expansive and beyond what we know as modern day Russia it covered a large area of both Europe and Asia. Also, it had expanded into North America and what is present day Alaska and even parts of Northern California and Hawaii. You can still visit Fort Ross, north of San Francisco, and see the base that Russia established during their expansion in 1812.
At its peak, the Empire included Belarus, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Finland, Ukraine, parts of Poland, and more.
7. Empire of Brazil

In 1822, Emperor Dom Pedro declared Brazil independent, separating it from Portugal and creating its own empire that covered what is not modern day Brazil and Uruguay. Dom Pedro was declared emperor as a way to differentiate himself from the King in Portugal and to make it seem more like Brazil truly was its own entity. Covering a swath of land that measured 8.3 million square kilometers or 3.2 million square miles, it was enormous and extremely hard to control.
Dom Pedro’s son, Dom Pedro II succeeded his father, and in what is an unusual twist from a historical standpoint, he had no interest in continuing rule beyond his lifetime. He did not feel that Brazil needed to have a monarchy and after a republican coup d’état to overthrow the government, neither Pedro nor his daughter had any interest in even trying to restore the monarchy.
6. Iberian Union
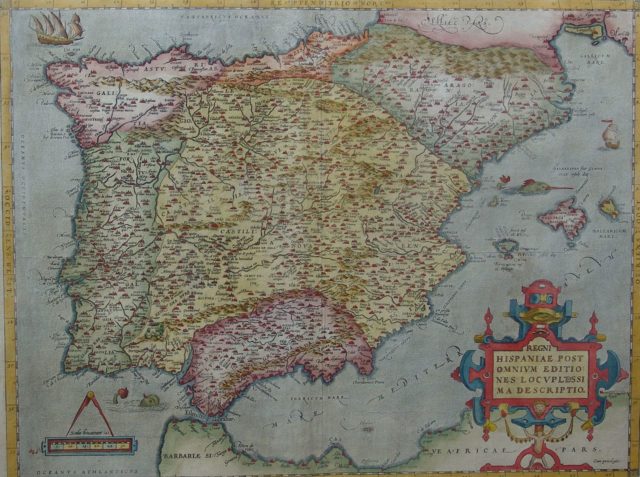
One of the more surprising empires in terms of size is the Iberian Union, if for no other reason than it really doesn’t get a lot of recognition in history classes. Despite that it covered over 7 million square kilometers, or 2.7 million square miles.
If you were to travel back to the 1500s and 1600s when the union existed, you would not find anyone who could tell you what the Iberian Union was, since historians invented the term in later years. But it referred to the political union between the kingdoms of Spain and Portugal that lasted for about 60 years.
Thanks to the union between the two, the Iberian peninsula and all of the territories overseen by Portugal fell under the purview of the Spanish Hapsburg kings. Portugal had been experiencing some turmoil thanks to the death of King Sebastian I and his only living heir. The succession crisis led directly to Spain’s involvement, and it would be sixty years until the Portuguese Restoration War established the House of Braganza as rulers and King John IV as the new king of Portugal.
5. Qing Dynasty
At 14.7 million square kilometers or about 5.7 million square miles, the Qing Dynasty in China was that country’s largest empire by far, although it’s arguable that the Mongolian Empire considered itself a Chinese empire as well.
As the last imperial dynasty of China, it lasted from 1644 until 1912. The Republic of China was established thereafter when Puyi, the last emperor, was forced to abdicate following the Xinhai Revolution.
The Qing Dynasty came about after the Ming Dynasty when Manchu people rose up against the Ming armies and occupied several cities. It would be a couple of decades before the Ming Dynasty was officially overthrown and Emperor Shunzhi established the Qing Dynasty in its place.
The new empire was actually fairly progressive at first, although many of the Han people now under its rule were not treated kindly. Emperor Kangxi established detailed maps, and a standardized dictionary. He lowered taxes and fought corruption. The empire expanded to include Taiwan and large parts of Siberia, greatly contributing to the massive size.
4. Abbasid Caliphate

Another empire often overlooked in Western history books, the Abbasid Caliphate covered over 11 million square kilometers, or 4.3 million square miles. This was the third caliphate after the prophet Muhammad and was named for his uncle.
The Abbasid caliphate overthrew the Umayyad caliphate in the year 750. They ruled until the Mongol Empire ended their reign in 1258. During that time, they ruled from Baghdad in what was known as the Golden Age of Islam. Science, medicine and philosophy were all major areas of advancement.
The areas ruled by the Caliphate included parts of Spain, Morocco, Italy, and the vast majority of the Middle East. Their control of these widespread realms was tenuous and did not last particularly long. By 756, only six years after the caliphate was established, they lost control of their Spanish territories, known then as al-Andalus, to the Umayyads who they had just overthrown.
3. Xiongnu Empire

One of the oldest empires, the Xiongnu Empire was established in 176 BC. It covered 9 million square kilometers or 3.5 million square miles. The empire was made up of nomadic people who lived across the Eastern Eurasian steppe. The land that they ruled was what we would now consider Mongolia and, in effect, that makes the Xiongnu the first Mongol Empire.
The origins of the Xiongnu people is still shrouded in mystery and it’s not known who exactly these people were. They were not considered Chinese by ancient Chinese scholars who wrote about them, and it’s been proposed at various times that the origins of the Xiongnu can be linked to Huns, Iran, and several others. They were considered one of what is known as the Five Barbarians by Chinese writers and were called the Hu people. Later, after the Han dynasty, that term became synonymous with the Xiongnu, but at the time it just referred to any nomadic people.
In 209 BC, the nomadic Xiongnu were all brought together under a new leader named Modu or Modun, depending on your sources. He was a chanyu, which was the title for supreme leaders of those people.
2. Spanish Empire

The Spanish Empire was the fifth largest empire in history and certainly gave the British Empire a run for its money for a time. It covered an area of 13.7 million square kilometers, or about 5.3 million square miles.
Historically speaking, the Spanish Empire is one of the most well known in modern times as it started in 1492, a date significant to the Western world as the year when Columbus sailed and discovered the Americas. Had it not been for that discovery and subsequent conquest by the Spanish, the empire would not have been nearly as large as it was. This colonization of these lands allowed them to control huge portions of not just Europe but Africa, the Americas, and the Philippines. The colonization of the Indies as well as parts of South America after conquering the Aztec and Inca people afforded the Spanish access to lands other empires had never even heard of.
The empire endured all the way until the mid-1970s when Spain finally relinquished control of some of its remaining colonies, including Spanish Sahara which it ceded back to Morocco.
1. French Colonial Empire

France may be the only country in the world that had two separate empires with just over a decade between them. The first colonial empire started in 1534 and lasted until 1814. The second colonial empire, which proved to be the larger of the two, started in 1830 when France took Algiers.
France claimed dominance over 11.5 million square kilometers of land, or around 4.4 million square miles. The first empire had lost most of its territories after engaging in a number of wars with Britain. The French Revolution, the Napoleonic Wars, and the American Revolution all resulted in a loss of land for France.
After the end of the Napoleonic Wars, Britain actually returned a number of territories to France, reestablishing their empire for the second time. France’s rule spread to places like Senegal, New Caledonia, Haiti, Vietnam and more.
Throughout the 1960s and ’70s France ceded control of many of the lands they had conquered back to their rightful owners, including Algeria and Vanuatu, which was the final country to regain its independence in 1980.