Humanity has flown people into outer space and landed them on the moon. We live in an age where we could go out and find other places to expand. But there are a few reasons we should continue to stay put, at least for a little while longer.
10. The Financial Cost
While it’s true that we currently have the capability to try to colonize distant worlds, the sheer amount of money that would go into such a venture could be just as astronomical. Some initial estimates point to around $150 billion to colonize Mars, and that’s the optimistic low end of the scale.
It doesn’t seem like that much considering the potential benefits to humanity in the long run, but with just a $120 billion investment we could halve the number of starving people worldwide. Money alone shouldn’t be the primary concern in any matter, but it’s a good representation of where we should invest our time and resources. We’re not saying we should never colonize the universe, but we should prioritize our needs before we start a new chapter in human evolution.
9. We Still Don’t Know Earth
The Earth’s surface is over 70% water. The oceans, which were once seen as impossible to traverse as deep space is today, still remain mostly unexplored. Over 95% of the depths have never been seen by human eyes, and with each passing day we discover new species of marine life which look as alien as aliens can get. Exploring the depths of the ocean could have some great and unexpected scientific benefits.
The ocean is very similar to the emptiness of space. Jacques Piccard and US Navy Lieutenant Don Walsh can both attest to the solitude and extreme pressures of the Mariana Trench when they descended into it in 1960. In fact, most space missions require initial water training. Sailing the bottom of the oceans could be a good exercise in learning how to better equip ourselves and survive the emptiness of space, all while discovering the remaining mysteries of our own planet.
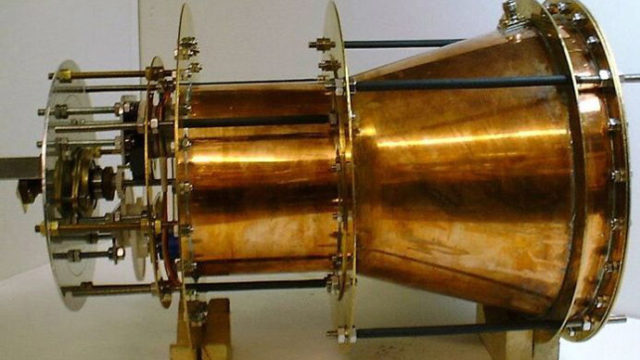
8. Unforeseen Risks and Developments
Nothing comes without risk, but this is especially true when it comes to leaving Earth. Even the smallest overlooked detail can turn into a tragedy, like in the case of the Challenger disaster. If we don’t take risks we’ll never get anything done, but we should take into account the developments made in rocket science on a daily basis. In 2014, a NASA research team confirmed a discovery made in 2006 by a British scientist, Roger Shawyer, where he achieved lift with the use of microwaves instead of rocket propellant. This groundbreaking discovery has turned the scientific community on its head, since it appears to goes against Newton’s third law of thermodynamics.
This new technology is still being tested and was only capable of producing minute amounts of lift, but if feasible it could revolutionize space travel. By not needing fuel, a disaster like Challenger could be avoided, not to mention that spacecraft could be much lighter and therefore carry more materials that would allow them to operate at a greater distance.
7. Measuring Distance With Time
Almost all scientists will agree that distance is actually measured with time. Space and time are not two different things, but one and the same. When we want to meet with someone, we always specify both a time and place since mentioning only one will get us nowhere. But humans operate with infinitesimally small numbers compared to what the Universe is used to.
An object moving at the speed of light, like a photon, will experience no time passing when traveling millions of light-years. The speed of light is the maximum allowed in the universe, and that photon travels that distance in an instant. What does this have to do with us staying put here on Earth, you ask? We need to consider the huge distances and times the Universe works with.
Let’s take Voyager 1, which is currently traveling at around 60,000 km/hour, and reached deep space after over 35 years of traveling through our Solar System. If it was headed towards the closest star, Proxima Centauri, some 4.3 light-years away, it would take it over 76,000 years to reach it. For perspective, human civilization began only 12,000 years ago. If we would stick around Earth until the highly theoretical Nuclear Pulse Propulsion becomes a reality, we would achieve that distance in just 85 years!
6. Gravity
You’re currently exerting a gravitational pull on the Andromeda Galaxy some 2.5 million light years away. Gravity is why we’re stuck to the ground, why the moon spins around the Earth and why our Sun and galaxy were created. It also attracts energy in the form of light. This can also be seen when a photon passes near a star, as its trajectory is slightly bent, or when it gets trapped in a black hole and never resurfaces.
Because all living things on Earth have evolved surrounded by our planet’s gravity, our bodies are designed to only work at maximum efficiency if experiencing a standard pull. Astronauts can feel the effects after a period in space. Since our bodies don’t have to do any work while in zero G, muscle mass can diminish at a rate of 5% per week, bone atrophies at 1% per month and the amount of blood in a body drops by 22%. Astronauts have to go through a rigorous physical training program prior to their departure, as well as when they’re up there and during the months they come back to Earth. In some cases, bones will never fully recover.
Colonists going to Mars will face challenges since after a seven month journey in zero G they’ll arrive on a planet with just a third of the Earth’s gravity and will have to build a colony in extremely unforgiving conditions. Keeping in mind that some astronauts are carried away on stretchers after just a couple of months in space, these colonists will be like a bunch of 80 year olds. That’s why NASA is conducting tests on human volunteers who lay in bed at a six degree inverted angle for 70 days to mimic the effect of zero gravity.
5. A.I.
Seeing what adverse effects the lack of gravity has on the human body, waiting for artificial intelligence doesn’t sound like a bad idea. Robots can aid future colonists by doing the heavy lifting and providing them with vital information. Scientists are developing robots that can fight fires autonomously, robots that can carry heavy loads on even the most treacherous of terrain, and cars that can drive themselves. Then there’s Watson, which is basically an accumulation of all human medical knowledge. All of these inventions could come in handy when colonizing other planets, but it may take some time before they’re totally reliable.
4. Cultural Melting Pot
Living in a globalized society has caused nationalities and races to blend together and form a unity of both culture and traditions. Take Britain, where 6% of children under the age of five have a mixed ethnic background, compared to only 3% for those between the ages of 20 and 24. Current day traditions and religions exist because of this mixing between different people throughout the ages.
One threat when talking about globalization is genetics. As Europeans first arrived in the Americas and over 90% of the indigenous population died because of disease, so too can a new plague wreak havoc among people who are genetically related. A modern, diverse society will also continue to show us its dark side with cases of discrimination, racism and intolerance, thus bringing us to our next point.
3. The Prime Directive
Popularized by Star Trek, the Prime Directive dictates that humanity, capable of interstellar travel, will not come in contact, disturb or influence the natural evolution of underdeveloped civilizations found on distant planets. What history and even the present day can attest to is that humanity will most certainly not follow the Prime Directive if faced with a technological inferior alien species. What we’re most afraid of in the event of a distant civilization visiting us will most likely be the same thing we would do to others if we were the visitors.
Moreover, if we were to find a planet capable of sustaining lifeforms like us, mere contact with that world would change it beyond recognition. If we were to leave just a single bacterium behind, that organism could multiply and mutate according to its new surroundings, altering that planet’s destiny forever and possibly even killing off already existing life. Finding such a world in the near future is next to impossible given our current level of technological advancement, but the simple idea of what we’re capable of doing to others less developed than ourselves could be enough to make us stick around Earth until we’re mature enough to deal with it.
2. Breaking the Status Quo
Humanity, despite the many conflicts happening around the globe, is experiencing its most peaceful era in history. Nevertheless, a new colony on a distant planet could bring the current status quo to an end. This future crisis could take decades if not entire generations to develop, but the question of how humanity will react to such a radical change to the modern status quo will always be looming in the background.
1. Taking Responsibility
History has shown us that many people only begin to change when they absolutely have to, and not a second sooner. It’s also a fact that the climate change Earth is experiencing is man-made, and thus people are turning their attention towards space travel and colonization for a solution. Starting anew is often the easy way out, but by not facing our problems head-on we’re doomed to repeat our mistakes wherever we go.
War, famine, discrimination, pollution and wastefulness are traits humanity should leave behind before starting to think about copying itself on distant worlds. We should make human life on Earth a functioning system that works in equilibrium with its surrounding environment before we decide to colonize other planets.









7 Comments
idk why people do the crazy things they do today. I think if people would just take care of earth we wouldn’t need a backup planet.
We will because of the cost of spending each second on earth, see, the universe is expanding so if we leave earth now, we will have an advantage, time and also because of overpopulation and lack of food resources. We would be better off living in a series of earth simulated spaceships.
I agree
What about when the sun explodes? Or when a meteor able to wipe out all life starts heading to earth? Or maybe even just when the next ice age comes
What about when your mom explodes that might happen soon
Ya joe your mom might explode, then you will get depression and commit die
i think that i could of been more to start of with and im in 7th grade>